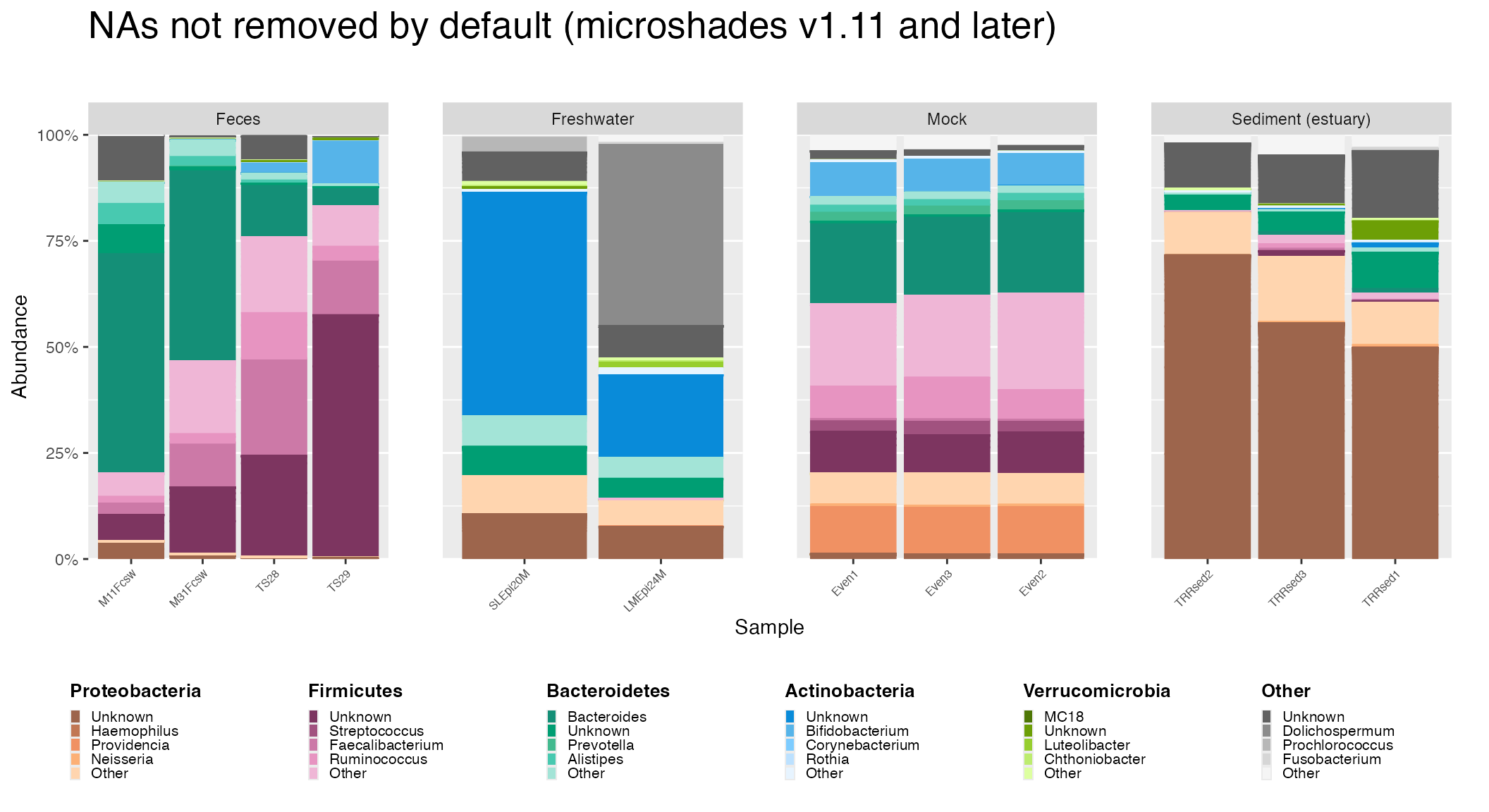
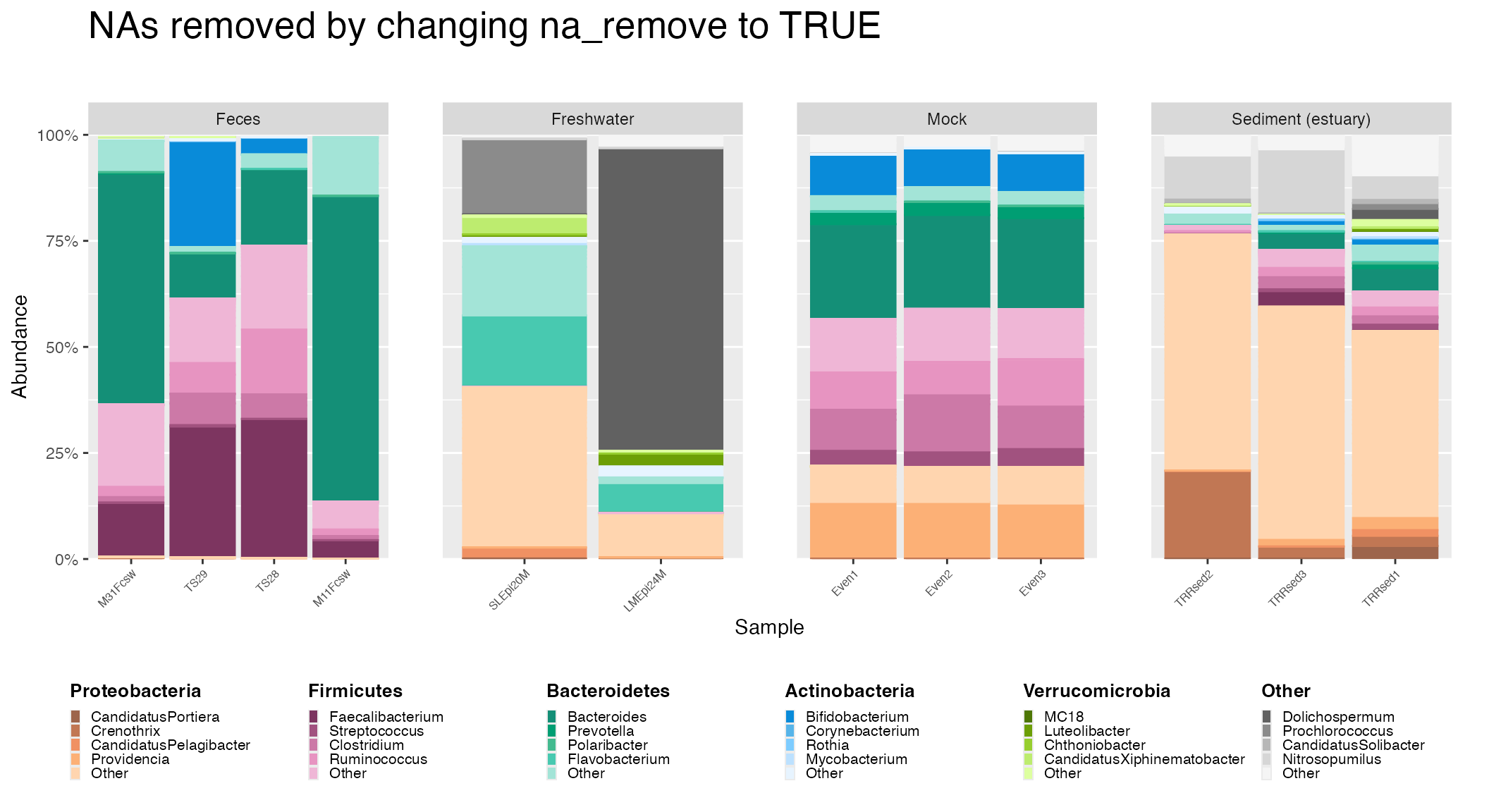
Remove NA Option
Anagha Shenoy, Lisa Karstens
June 6, 2024
Source:vignettes/remove_na_option.Rmd
remove_na_option.RmdThe microshades package allows for color organization in
data visualizations, particularly visualizations of microbiome data.
Relative abundance plots are common to microbiome investigations as they
present an informative overview of the bacterial composition of
samples.
Previously, the default microshades behavior in versions
1.1 and earlier was such that NA values in the input data (a phyloseq
object) were ignored. That is, relative abundances were calculated as
though bacteria that are not identified taxonomically are not present in
the sample. For more details on the issue and origin of the behavior,
see issue
18.
The default behavior of microshades in versions 1.11 and
later is NOT to remove NA values. If users wish to remove NAs , the
prep_mdf function has a remove_na parameter to
allow users to specify whether or not NA values should be removed from
the data during the taxa agglomeration step.
Removal of NA values can affect interpretation of data depending on what dataset is examined. The following example demonstrates this in addition to demonstrating how to remove NAs when using microshades.
Code to generate default plot with NAs
mdf_GP_updated is the object to be plotted. It contains
the abundance information organized by taxa (phylum and genus in this
example), with NA values not removed. cdf_GP_updated will
be used for coloring the plot.
mdf_updated <- prep_mdf(GlobalPatterns) # prep_mdf function to agglomerate, normalize, melt
# Create abundance dataframe & color mapping dataframe
color_objs_GP_updated <- create_color_dfs(mdf_updated,
selected_groups =
c("Verrucomicrobia", "Proteobacteria", "Actinobacteria", "Bacteroidetes",
"Firmicutes"),
cvd = TRUE)
mdf_GP_updated <- color_objs_GP_updated$mdf
cdf_GP_updated <- color_objs_GP_updated$cdf
# Order the samples by Proteobacteria abundance for visual organization
reordered_GP_update <- reorder_samples_by(mdf_GP_updated,
cdf_GP_updated,
order = "Proteobacteria",
group_level = "Phylum",
subgroup_level = "Genus",
sink_abundant_groups = TRUE)
# Extract dataframes
mdf_up_GP <- reordered_GP_update$mdf
cdf_up_GP <- reordered_GP_update$cdf
mdf_up_GP <- mdf_up_GP %>% subset(SampleType %in% c("Feces", "Freshwater", "Mock", "Sediment (estuary)"))
legend <- custom_legend(mdf_up_GP, cdf_up_GP, legend_orientation = "horizontal")
center_legend <- plot_grid(NULL, legend, nrow=1, rel_widths=c(0.04, 0.96))
plot_updated <- plot_microshades(mdf_up_GP, cdf_up_GP)
faceted_plot_updated <- plot_updated +
scale_y_continuous(labels = scales::percent, expand = expansion(0)) +
theme(legend.position="none") +
facet_wrap(~SampleType, scales = "free_x", ncol=4) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(size = 6)) +
theme(plot.margin = margin(6,20,6,6)) +
theme(plot.title = element_text(size = 20, margin=margin(0,0,30,0))) +
theme(panel.spacing = unit(2, "lines")) +
ggtitle("NAs not removed by default (microshades v1.11 and later)")Code to generate plot with NAs removed
To remove NAs, the remove_NA parameter is set to
TRUE when calling the prep_mdf function.
mdf_prep <- prep_mdf(GlobalPatterns, remove_na = TRUE) # NAs to be removed
# Create abundance dataframe & color mapping dataframe
color_objs_GP <- create_color_dfs(mdf_prep,
selected_groups =
c("Verrucomicrobia", "Proteobacteria", "Actinobacteria", "Bacteroidetes",
"Firmicutes"),
cvd = TRUE)
# Extract dataframes
mdf_GP <- color_objs_GP$mdf
cdf_GP <- color_objs_GP$cdf
# Order the samples by Proteobacteria abundance for visual organization
reordered_GP <- reorder_samples_by(mdf_GP,
cdf_GP,
order = "Proteobacteria",
group_level = "Phylum",
subgroup_level = "Genus",
sink_abundant_groups = TRUE)
# Extract dataframes
mdf_re_GP <- reordered_GP$mdf
cdf_re_GP <- reordered_GP$cdf
mdf_re_GP <- mdf_re_GP %>% subset(SampleType %in% c("Feces", "Freshwater", "Mock", "Sediment (estuary)"))
facet_legend <- custom_legend(mdf_re_GP, cdf_re_GP, legend_orientation = "horizontal")
center_facet_legend <- plot_grid(NULL, facet_legend, nrow=1, rel_widths=c(0.04, 0.96))
plot <- plot_microshades(mdf_re_GP, cdf_re_GP)
faceted_plot <- plot +
scale_y_continuous(labels = scales::percent, expand = expansion(0)) +
theme(legend.position="none") +
facet_wrap(~SampleType, scales = "free_x", ncol = 4) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(size = 6)) +
theme(plot.margin = margin(6,20,6,6)) +
theme(plot.title = element_text(size = 20, margin=margin(0,0,30,0))) +
theme(panel.spacing = unit(2, "lines")) +
ggtitle("NAs removed by changing na_remove to TRUE")